
The crypto market has its own set of terms for certain things; once you understand these terms well enough, it can help you make smarter trading decisions. Otherwise entering crypto trading without knowing these terms will feel like a new language. You may be a beginner or experienced but willing to develop your trading skills or either, learning these trading terms is important to understand the crypto market.
In this final guide, we’ll walk you through the most important crypto trading terms you must know in 2025, from market types to technical indicators.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Trading Terms:
1. Cryptocurrency

It is important to know what cryptocurrency is before getting into the market of crypto trading. A cryptocurrency is a virtual or digital currency that is used for cryptography. The most popular and established cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum (ETH), and Solana (SOL). These coins operate on decentralized networks using blockchain technology.
2. EXCHANGE

A digital platform where you can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies is a crypto exchange. There are two main types of exchanges:
Centralized Exchanges (CEX): Platforms like Bitcoin or Coinbase, where a third party helps the trade.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX): Sites like Uniswap or PancakeSwap that depend on smart contracts and allow peer-to-peer transactions.
It is important to know how exchanges function in order to trade safely and effectively.
3. Wallet

A crypto wallet stores your money digitally. There are two types:
- Hot Wallets: Connected to the Internet (mobile app, computer)
- Cold Wallets: Offline wallets (Hardware wallet) that are safer.
Always know how to keep your wallet safe and secure to protect your money.
Read More: Best crypto wallets and exchanges in the uae: Secure ways to store and trade
4. Trading Pair
The market between two currencies is called a trading pair.
For example, in BTC/USDT:
- You sell or buy Bitcoin with USDT (Tether), which is a stablecoin.
Knowing trading pairs allows you to choose the right market to trade.
5. Market Order vs. Limit Order

These are two common order types:
- Market Order: Fills instantly at the best current price.
- Limit Order: Fills only when the money reaches a price you want.
There are advantages to each of these order types, depending on your approach and goals.
6. Bid and Ask Price

- Bid Price: The most an investor is willing to pay.
- Ask Price: The least a seller will take.
7. Bull Market vs. Bear Market

- Bull Market: A rising market or one expected to rise.
- Bear Market: A declining market or one expected to decline.
Knowing whether you are in a bull or bear market helps you make better decisions on when to get in and out of trades.
8. Long and Short Positions

- Long Position: You buy an asset with hope that its price will rise.
- Short Position: You short an asset (typically borrowed) in expectation that its price drops and you can buy it back at a cheaper price.
9. Leverage
Leverage allows you to open a larger position than your real money. For example, if there is 10x leverage, a $100 investment can manage $1,000 worth of crypto.
Leverage increases potential reward and risk alike. Care must be taken in using it.
10. Margin

Margin is the security you use to borrow money for leveraged trading. If the market goes against your position, you might be subject to a margin call where you need to fill more money or get liquidated.
Read Also: What Is Margin Trading in Crypto? Explained for Beginners
11. Liquidity

Liquidity refers to how easily an asset can be bought or sold without impacting its price. Liquid assets have a lot of buyers and sellers floating around, making it easier and faster to trade.
12. Volume

Trading volume indicates the volume of a cryptocurrency that has been traded over a given period. The greater the volume, typically the greater the interest and activity within the market.
Volume can confirm the authority of a price move rising volume with rising prices is a very strong bullish sign.
13. Volatility
Volatility measures how much an asset’s price changes. Crypto markets are extremely volatile, and prices move very fast. This means opportunities as well as danger.
14. Stop-Loss and Take-Profit

- Stop-Loss: A command to sell an asset if the price falls to a certain level. It helps manage the halting of losses.
- Take-Profit: A command to sell when a target price is reached in order to lock in profits.
These instruments will be mastered to ensure risk management when trading crypto.
15. Support and Resistance
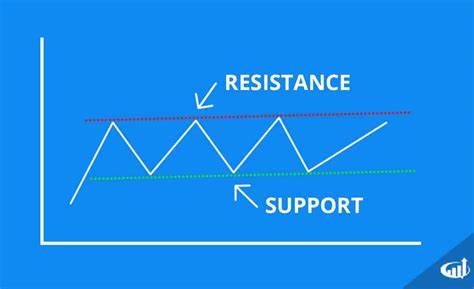
- Support: A price level at which a falling asset will halt its fall and may rise again.
- Resistance: A price level at which a rising asset will halt its rise and may drop.
These levels are the foundation of technical analysis and are used to predict market movement.
16. Technical Analysis (TA)

Technical analysis is the examination of price charts and trading volume in expectation of future price movement. Some common tools include:
- Candlestick patterns
- Moving averages
- Relative Strength Index (RSI)
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Knowledge of TA provides you with a data-based advantage when making trading decisions.
17. Fundamental Analysis (FA)
Fundamental analysis involves assessing the real value of a cryptocurrency by examining factors such as:
- Project development
- Use cases
- Team background
- Adoption rate
- News and regulations
This is especially useful for long-term investments.
18. Altcoin

Any cryptocurrency that is not Bitcoin is considered an altcoin. Some examples are Ethereum, BNB, Cardano, and Polygon.
Various altcoins are used for different purposes, ranging from smart contracts to payments or NFTs.
19. Stablecoin

A stablecoin is a cryptocurrency that is meant to have a stable value, most commonly fixed to fiat currencies such as USD. Some examples are USDT, USDC, and DAI.
Traders uses stablecoins for value storage and to limit the exposure to volatility in market dips.
20. Tokenomics

Tokenomics is a combined word of “token” and “economics.” Tokenomics is the supply and demand, and usage rules, for a cryptocurrency token. Variables are:
- Maximum supply
- Circulating supply
- Distribution model
- Inflation/deflation mechanism
Good tokenomics promote long-term value of a project.
21. Gas Fees

Gas fees are fees you pay on blockchain networks like Ethereum. They pay miners or validators to process and secure transactions.
Gas fees might fluctuate with network congestion.
22. DYOR (Do Your Own Research)

DYOR is the first rule of crypto trading. It means researching an asset or project before investing. Relying on tips or hype alone can be dangerous.
23. FOMO and FUD

- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): Trading based on excitement or hype.
- FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt): Negative news or rumors causing panic selling.
Understanding your emotional triggers stops you from making impulsive mistakes.
24. HODL

HODL is a typo of the term “hold” but is used today to describe holding cryptocurrency assets long term, regardless of what occurs in the markets.
It is a statement of confidence in the future value of the asset.
25. Whales

Whales are institutions or entities with significant positions in cryptocurrency. Their trades can shift markets in meaningful directions.
Watching whale trades can give clues on probable price movements.
CONCLUSION
By understanding these key crypto trading terms, you’re not only expanding your vocabulary but also becoming a trader’s mind. Each word is assisting you in making a more informed decision, protecting your investments, and taking advantage of opportunities in the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies.
As you proceed to travel in 2025 and beyond, continue learning, stay alert, and trade all the time with a strategy mapped out in your head. The crypto universe rewards the educated, disciplined, and flexible.
